
Concepts to Cover Today:
- Earth’s Internal Structure – Layers of the Earth
- Plate Tectonics – Theory, Types of Plates, and Their Movements
- Earthquakes & Volcanoes – Causes and Effects
- Mountain Building & Landforms
- 50 MCQs on Earth’s Structure & Plate Tectonics: Click Here
1. Earth’s Internal Structure
Earth is divided into three main layers based on chemical composition:
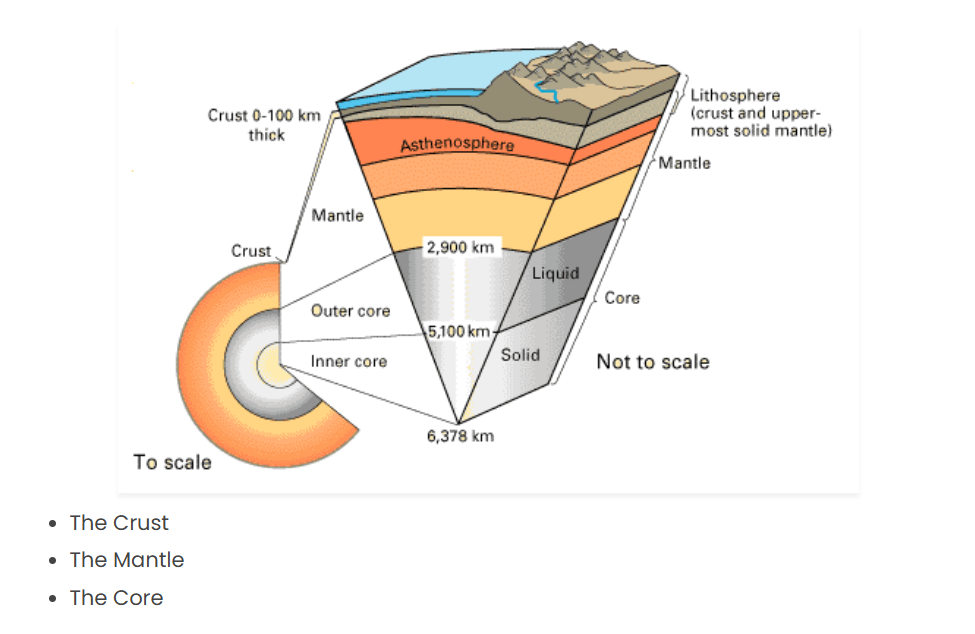
- Crust – Outermost layer (continental & oceanic crust).
- Mantle – Middle layer, semi-solid, rich in silicate minerals.
- Core – Innermost layer, mostly iron & nickel (divided into outer liquid core & inner solid core).
👉 Key Points:
✅ Crust: Thinnest layer (~5-70 km thick).
✅ Mantle: Largest layer (80% of Earth’s volume).
✅ Core: Responsible for Earth’s magnetic field due to the movement of molten iron.
BNC Academy’s Notes: Click Here
2. Plate Tectonics – The Driving Force
The lithosphere (crust + upper mantle) is divided into several plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere.
👉 Types of Tectonic Plates:
🔹 Major Plates: Pacific, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, African, Antarctic, North American, South American.
🔹 Minor Plates: Arabian, Philippine, Cocos, Nazca, etc.
Plate Boundaries & Movements
- Divergent Boundary – Plates move apart (Mid-Atlantic Ridge).
- Convergent Boundary – Plates collide (Himalayan Mountain Formation).
- Transform Boundary – Plates slide past each other (San Andreas Fault).
📌 Illustration of Plate Movements: Click here
📖 Reference Links:
3. Earthquakes & Volcanoes
👉 Earthquakes: Sudden release of energy due to movement along faults.
🔹 Measured by Richter Scale & Mercalli Scale.
🔹 Seismic waves – P-waves, S-waves, Surface Waves.
🔹 Most earthquakes occur in Ring of Fire.
👉 Volcanoes: Openings in Earth’s crust that allow magma to escape.
🔹 Types: Shield (Hawaii), Composite (Mt. Fuji), Cinder Cone.
🔹 Active, Dormant, Extinct Volcanoes.
📌 Best Link to Study Earthquakes & Volcanoes: Click here
4. Mountain Building & Landforms
- Fold Mountains – Himalayas, Alps (Formed due to collision of plates).
- Block Mountains – Black Forest (Germany), Sierra Nevada (USA).
- Volcanic Mountains – Mount Fuji, Mount Kilimanjaro.
👉 Key Takeaway:
- Tectonic processes shape Earth’s surface.
- Geographical features like mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes are all interrelated.
📌 Illustration of Mountain Formation: Click here
💡 Practice for Today
✅ Revise Class 11 NCERT Geography Chapters 1 & 2
✅ Solve 10 Previous Year UPSC Questions on Plate Tectonics
✅ Make a one-page mind map on Earth’s Structure & Plate Movements
✅ Watch a 12-minute video on Plate Tectonics (Click Here)
💪 Moral Strength & Motivation
🌟 UPSC is tough, but so are you!
🌟 Every topic you cover takes you one step closer to your dream.
🌟 Consistency beats talent when talent doesn’t work hard.
🔥 Remember: The Earth took millions of years to shape itself into what it is today. Your preparation is similar. Step by step, layer by layer, you are building a strong foundation.
Keep going. Your success is inevitable! 🚀💯
